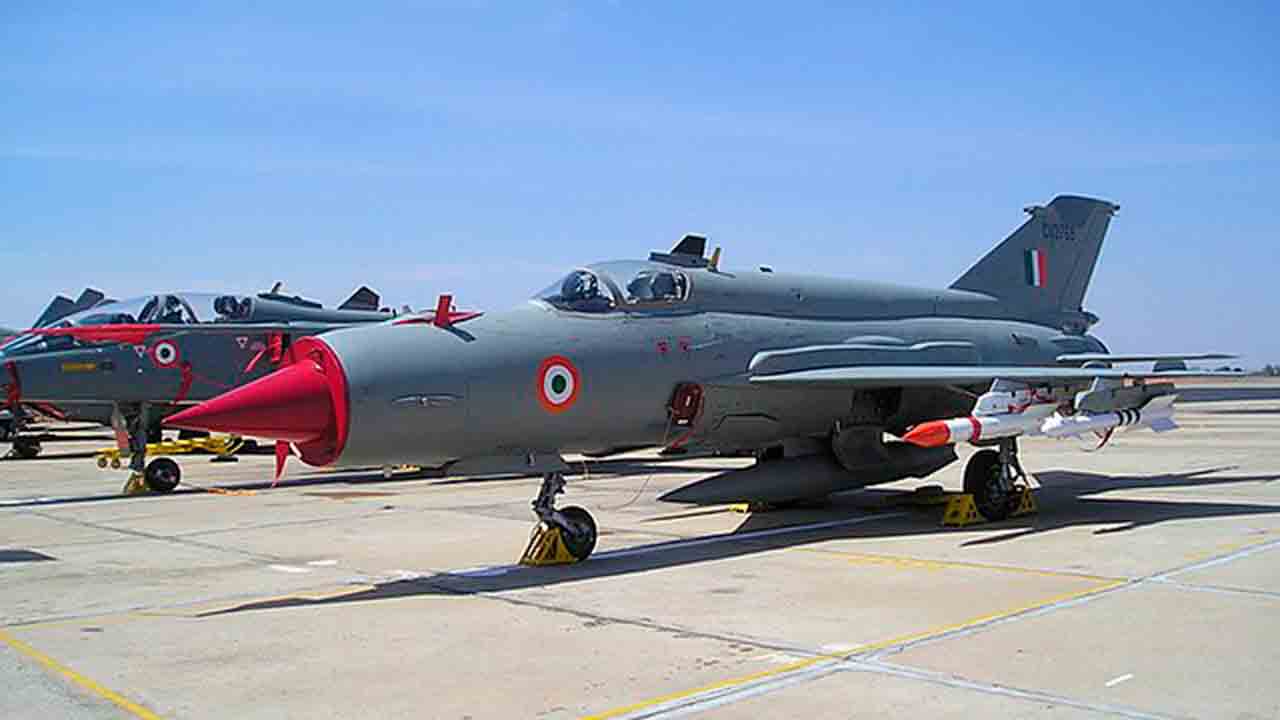
The MiG-21, known as “Fishbed” by NATO, is one of the most iconic fighters in military aviation history. Designed by Mikoyan-Gurevich in the Soviet Union, the MiG-21 is a second-generation multirole jet fighter that set records in both performance and production.
+ Polish Air Force F-35A Lightning II Takes Off for the First Time
+ Tense Video: Airbus A321neo Struggles Against Wind While Attempting to Land in Chennai, India
Technical Details
-
- Type: Interceptor and multirole fighter aircraft.
- Origin: Soviet Union.
- First Flight: June 16, 1955.
- Service Entry: 1959.
- Maximum Speed: 2,175 km/h (Mach 2.05).
- Service Ceiling: 19,000 meters.
- Range: Approximately 1,200 km.
- Engine: Tumansky R-25 turbojet (in advanced models).
- Armament:
- 23 mm autocannon.
- Air-to-air missiles (K-13, R-3S, and others).
- Bombs and rockets for ground attacks.
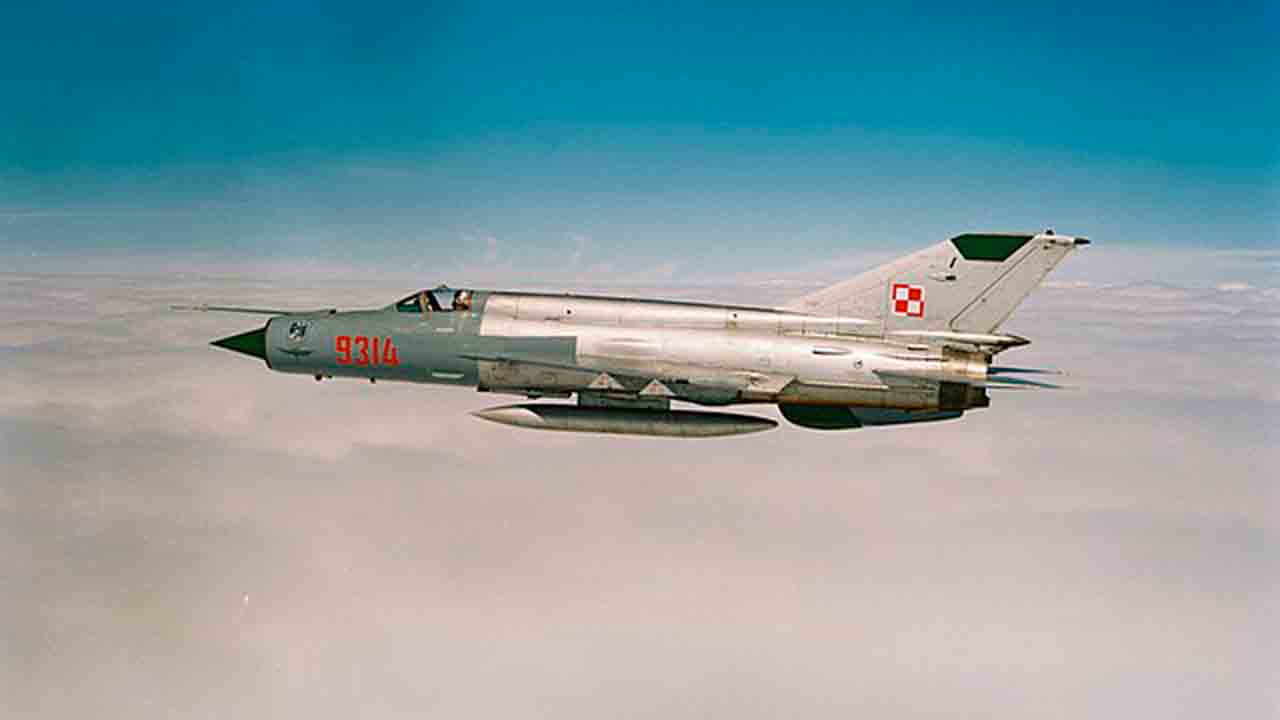 MiG-21 from the Polish Air Force. Photo: Wikimedia
MiG-21 from the Polish Air Force. Photo: Wikimedia
Main Versions
The MiG-21 had numerous versions adapted for various missions and technological upgrades:
- MiG-21F: The first production version with an internal cannon and limited armament capacity.
- MiG-21PF: A version without an internal cannon but equipped with radar for all-weather interception.
- MiG-21R: A reconnaissance version equipped with cameras and sensors.
- MiG-21MF: A multirole version widely exported with enhanced combat and armament capabilities.
- MiG-21bis: The final and most advanced version, featuring improved performance and combat capabilities.
- MiG-21U/UM/US: Training versions with dual cockpits.
Interesting Facts
- Massive Production: The MiG-21 is the most-produced supersonic fighter jet in history, with over 11,000 units built between 1959 and 1985.
- Operators: It was used by over 60 countries, from major powers to smaller nations. It remains in service in some countries.
- Conflicts: The MiG-21 participated in major conflicts, including the Vietnam War, Yom Kippur War, Gulf War, and various conflicts in Asia and Africa.
- Agility: Although light and fast, it had limitations in close air combat due to its short range and limited sensors.

Accidents and Limitations
- High Accident Rate: Due to its simple design and large-scale production, the MiG-21 faced high accident rates, especially in air forces with less experience or resources. Maintenance errors and insufficient training were common factors.
- Fuel and Range: It had limited range, requiring constant support from bases or ground refueling.
- Sensors and Armament: In combat, particularly against more modern aircraft, its outdated technology limited its effectiveness.
Notable MiG-21 Accidents
- India: As a long-time MiG-21 operator, India faced numerous accidents with the model. Between 2000 and 2020, over 400 MiG-21s were lost, earning it the nickname “flying coffin.”
- Vietnam War: While it excelled in engagements against U.S. fighters, many MiG-21s were lost due to surprise attacks and radar limitations.
- African Countries: Operators with limited infrastructure often suffered losses due to mechanical failures and accidents.

Legacy
The MiG-21, with its simplicity, speed, and affordability, transformed the military aviation landscape during the Cold War. Despite its limitations, the fighter remains a significant piece of military and aeronautical history. It symbolizes both the challenges and advancements of an era where air superiority was crucial to global strategic dominance.
Photos: Wikimedia. This content was created with AI assistance and reviewed by the editorial team.