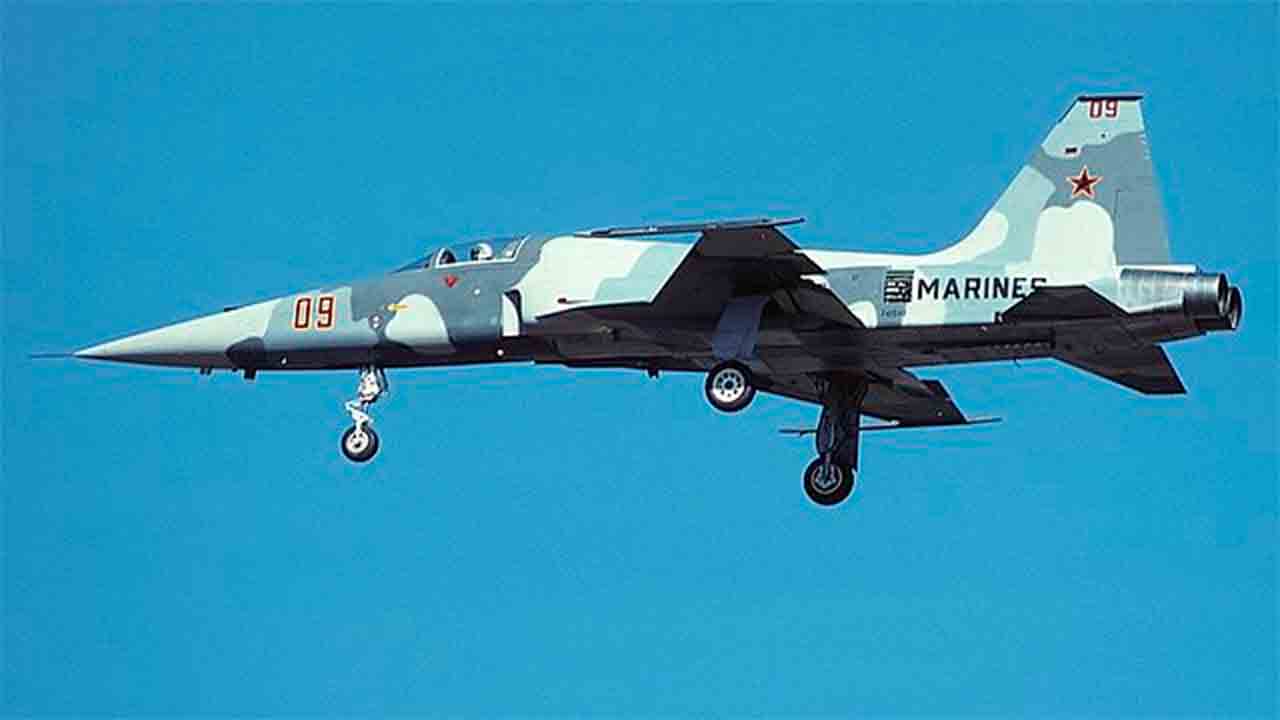
The Northrop F-5 is a lightweight, agile, and versatile fighter jet that has become a benchmark in military aviation since its introduction in the 1960s. Designed in the United States by the Northrop Corporation, the F-5 was developed as a cost-effective combat aircraft, ideal for allied nations that could not afford more expensive jets like the F-4 Phantom.
Development
The F-5 emerged from Northrop’s studies in the 1950s on creating a lightweight and affordable jet for export. The company used cost-effective and reliable components, such as the General Electric J85 engines, originally developed for missiles.
- First Flight: The prototype, named N-156, first flew on July 30, 1959.
- Objective: To provide a combat platform for allied nations in the context of the Cold War.
- Design: Compact, twin-engine, with an excellent power-to-weight ratio, offering high maneuverability.
The initial model was produced as the F-5A Freedom Fighter and quickly gained popularity among U.S. allies, with exports to numerous countries.
GE J-85 Engine
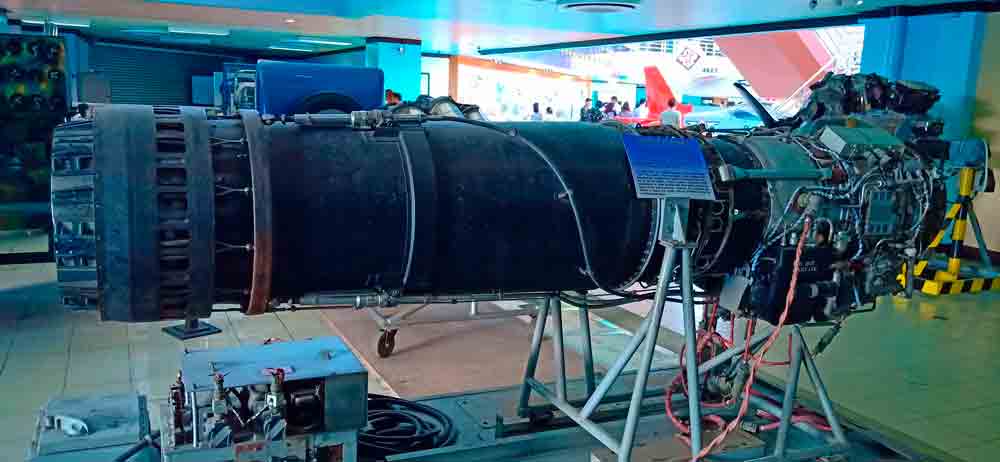

The J85 is a compact and lightweight turbojet engine designed to deliver a high power-to-weight ratio, essential for small jets like the F-5.
Specifications of the J85-GE-21 (F-5E/F Tiger II)
- Type: Axial turbojet
- Thrust without afterburner: Approximately 13.8 kN (3,100 lbf)
- Thrust with afterburner: Approximately 22.2 kN (5,000 lbf)
- Length: 1.29 meters
- Diameter: 0.45 meters
- Weight: About 180 kg
- Airflow rate: 23 kg/s
- Specific fuel consumption:
- With afterburner: 2.15 kg/(h·kN)
- Without afterburner: 1.0 kg/(h·kN)

Variants
The F-5 has seen various versions developed over the years to meet specific combat and training requirements.
- F-5A Freedom Fighter (Introduction: 1962)
- Original version designed for light attack missions and interception.
- Weapon load capacity: Missiles, bombs, and rockets on five hardpoints.
- Exported to over 30 countries.
- F-5B
- Two-seat training version with limited combat capability.
- Used to train pilots for flying the F-5A.
- F-5E Tiger II (Introduction: 1972)
- An evolution of the F-5A with extended range, improved radar, and advanced electronics.
- Engines upgraded to more powerful versions.
- Became the most popular variant.
- F-5F
- Two-seat training version of the F-5E.
- Retains the combat capabilities of the Tiger II.
- F-5G (F-20 Tigershark)
- Advanced prototype of the F-5 with modernized radar and engines.
- Despite its superior capabilities, the F-20 did not enter production due to competition from models like the F-16.
- Modernizations
- Many countries have modernized their F-5s with advanced avionics, modern radars, and guided weapons, keeping the aircraft relevant even decades after its introduction.
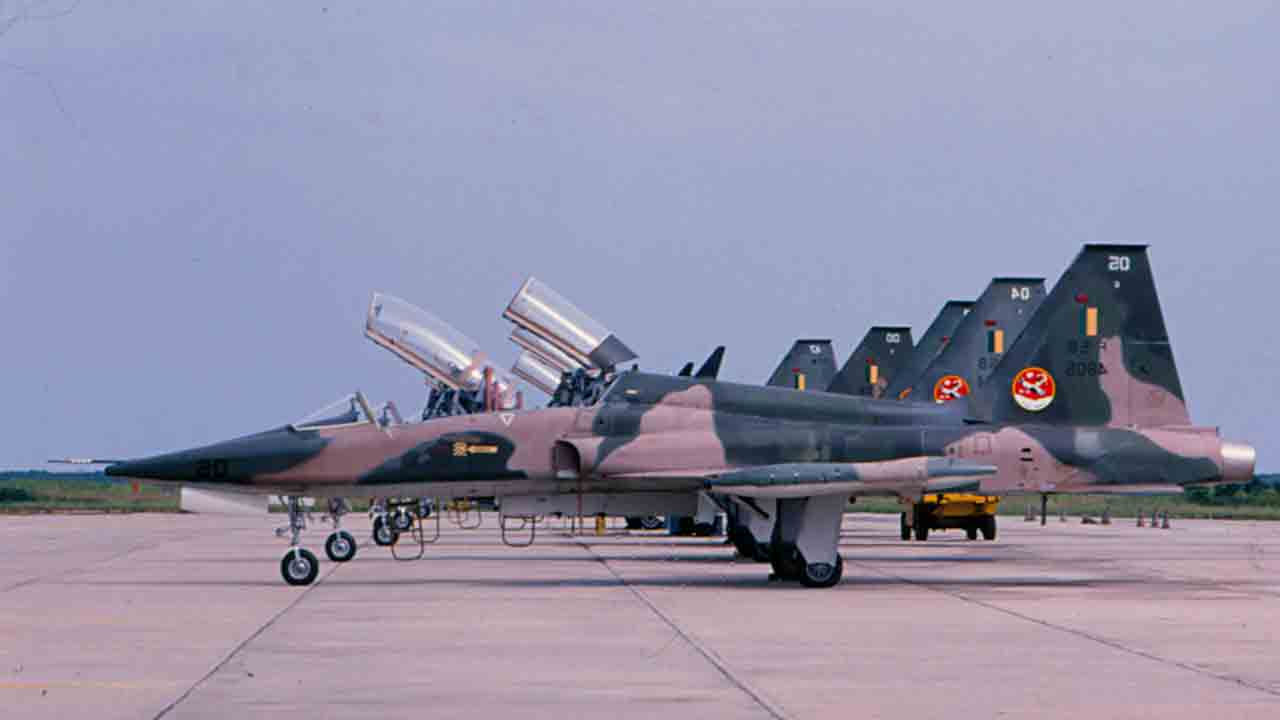

Countries Still Operating the F-5
Despite being designed over 60 years ago, the F-5 remains operational in several countries thanks to its simplicity, low maintenance costs, and ease of modernization.
- Brazil
- Uses the F-5EM/FM, modernized versions with Israeli radars and updated systems.
- The Brazilian Air Force employs the F-5 as its primary fighter until the Gripen E is introduced.
- Taiwan
- Modernized its F-5s for advanced training and secondary air defense missions.
- Switzerland
- Uses the F-5E for training and air patrol missions.
- South Korea
- Operates F-5Es for light attack missions and training.
- Thailand
- Modernized its fleet for attack and defense missions.
- Iran
- Still operates a large fleet of F-5s with various local modifications.
- Turkey
- Uses the F-5 for training missions and in the Turkish Stars aerobatic team.
- Other Countries
- Mexico, Morocco, Chile, the Philippines, and others continue to use the F-5 in secondary roles.
Interesting Facts
- Affordable Price: The relatively low cost made the F-5 a popular choice for air forces in developing nations.
- Aerobatic Teams: The F-5 was widely used by aerobatic teams like the U.S. Thunderbirds and Turkey’s Turkish Stars.
- Movie Appearances: Gained fame in the movie Top Gun, representing enemy fighters.
The F-5 remains an iconic aircraft, showcasing how simple and effective design can ensure operational longevity. Even with the introduction of fifth-generation jets, the F-5 continues to be relevant in air forces around the world.
Photos: flickr / Wikimedia. This content was created with AI assistance and reviewed by the editorial team.